Transparency

The following report is produced in accordance with the Regulation of the Financial Supervisory Authority (FSA) no. 2/2016 on the implementation of corporate governance principles by entities authorized, regulated and supervised by the FSA, with the subsequent amendments and completions.
In light of the requirements of the regulations set out above, PAID S.A. publishes and periodically updates the information subject to disclosure requirements.
Download the document in PDF format.
A. Organizational structure
The leadership and management of the company is made up of: the General Assembly, the Board of Directors, the Chief Executive Officer and the Deputy Chief Executive Officer.
Company shareholders:
The company shareholders hold together 19,341,819 shares in the company’s stock with a nominal value of 4 Lei, so currently the share capital of PAID S.A. is 77,367,276 Lei.
Given the amendments to Law 260/2008 effective starting November 11, 2023, PAID's shareholding is available for entities other than insurers and the maximum holding has increased from 15% to 25% (30% for groups).
The five members of the Board of Directors are:
Executive Management:
In carrying out its activities, the management structure benefits from the support of nine advisory boards. These operate according to organizational and operational regulations and make recommendations on various topics subject to the decision-making process and forward materials/reports to the Board of Directors on matters entrusted by it.
These boards are: the Risk management committee, the Audit committee, the Insurance Claims committee, the Complaints and dispute analysis and resolution committee, the Investment committee, the Reinsurance committee, the Business continuity steering committee, the Remuneration committee and the Crisis committee for the disaster damage instrumentation plan.
The people holding key leadership roles are: the Head of Risk Management Department, the Chief Compliance Officer, the Head of Internal Audit: role outsourced to Deloitte Audit SRL - Manager responsible for outsourcing the role: the Head of the Internal Audit Department.
Organizational structure:
B. The main features of the governance system
The governance system comprises organizational structures designed to support achieving strategic goals and the activity of the company. PAID S.A is properly and efficiently organized and all necessary operational procedures and controls are implemented. PAID's governance system is based on a proper and transparent responsibility distribution, which targets an effective decision-making process, preventing conflicts of interest and ensuring the efficient management of the company.
There are multiple systems within the company that are meant to achieve corporate governance, such as:
A series of policies and procedures were also adopted and implemented at company level, including policies to ensure smooth business operations; appropriateness policies; remuneration policies; information security policies; outsourcing policy; the Solvency II policy etc. These are subject to a regular review and approval process, taking into consideration the nature, scale and complexity of the activities at an individual and corporate level.
The Company’s objectives regarding the corporate governance system are focused primarily on:
The organizational chart of the company and the Organizational and operational guidelines prove that the company has a structure suited for its nature, volume and complexity and the principle of proportionality is respected. The Organizational and operational guidelines also mention the roles and duties of the company's organizational structures.
In the reporting period, changes were made to the organizational structure to reflect the adjustments within the organization following the changes regarding the role of Deputy Chief Executive Officer and the reassignment of duties, but also the changes within the organization determined by the increasing complexity of the business following the amendment of Law 260/2008.
The business model complexity increased with the amendment of Law 260/2008, requiring a balanced responsibility assignment in order to ensure the necessary coordination and operation capacity.
The changes were based on the following considerations:
Thus, the Deputy Chief Executive Officer/CDO (Chief Development Officer) role was created, coordinating the operational (Insurance Claims, IT) and development areas (Marketing, Underwriting and Distribution).
Further details on the corporate governance framework are available in the Solvency and Financial Condition Report (SFCR) Ch. B.
C. Financial position assessment conclusions
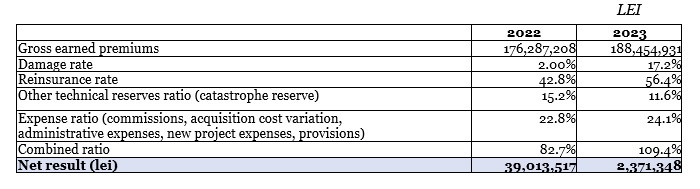
The main financial indicators of the company, according to the statutory accounting and financial reporting standards:
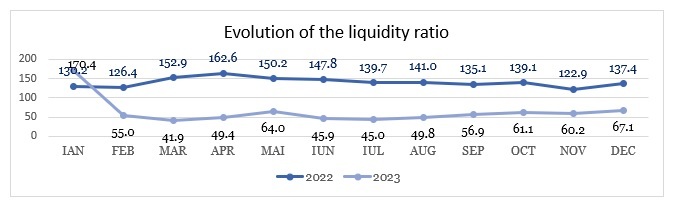
Evolution of the liquidity ratio, defined and determined in accordance with ASF’s methodology:
The main financial soundness indicators of the company, according to the Solvency II reporting regime, calculated using the standard formula:
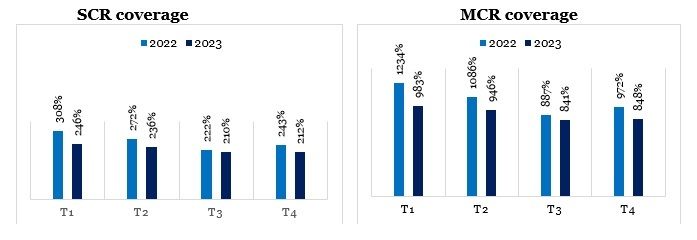
From 2022, the solvency ratio showed a downward trend determined by the increase of the SCR mainly as a result of the increase of retention and the company’s exposure by extending the portfolio. The market value of government bonds remains lower than the carrying value because of the unfavorable evolution of the interest rate.
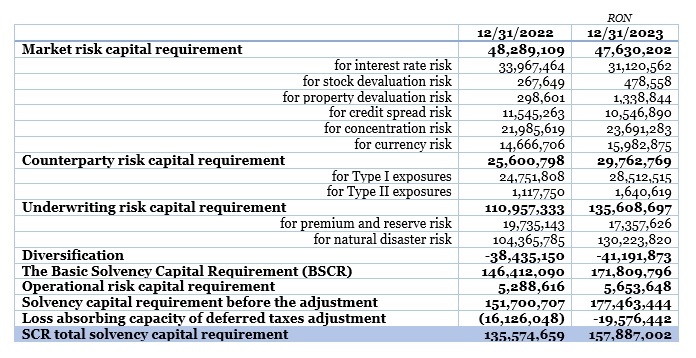
The solvency capital requirement (SCR) on 12/31/2023 is 157,887,002 RON. The solvency ratio is 212% after paying dividends.
To cover for catastrophe risks, on 12/31/2023, PAID S.A. had an active reinsurance program with a capacity of 1 billion EURO for earthquake, flood and landslide risks, with a retention of up to 13 million EURO for earthquake risks and 9 million EURO for flood and landslide risks. The reinsurance program is endorsed by a panel of 52 reinsurers and around 45% (according to the theory of second best) of its capacity comes from reinsurers with “AA” ratings assigned by S&P or AM Best.
D. Main features of the formal framework for the implementation of financial reporting principles and practices
PAID S.A. draws up statutory financial statements in accordance with Regulation 41/2015 of the Financial Supervisory Authority for the approval of the Accounting regulations regarding annual individual and consolidated financial statements of entities conducting insurance and/or reinsurance activities.
Annual financial statements are audited by an independent auditor. The financial reporting package for fiscal year 2023 was audited by Mazars România SRL.
Reporting under Solvency II (SII)
In accordance with the financial reporting requirements of Law 237/2015 on the authorization and supervision of insurance and reinsurance activities and of Regulation 21/2016 regarding insurance and/or reinsurance activity reports, with further amendments and completions, PAID S.A. draws up and reports:
In addition, in accordance with the provisions of the Solvency II Directive, the Commission Delegated Regulation and the internal policy, PAID S.A. draws up an own risk and solvency prospective assessment report (the ORSA report) annually or whenever important changes occur in its risk profile or risk appetite.
The Reporting policy was developed and applied to PAID S.A., policy whose purpose is to ensure the timely generation and forwarding of all mandatory reports, as well as their correctness and completeness.
The Audit committee is the forum that approves statutory and Solvency II reports before they are sent for approval to the Board of Directors and/or the General Assembly, as applicable.
E. Main features of the risk management system
The risk management system at the company level is implemented by planning, coordinating and controlling risk management activities. Within this system, specific strategies are created, policies and procedures are developed for the timely identification, assessment, monitoring, management/reduction and reporting of risks in order to optimize them and to create a “risk-aware” organizational culture.
The purpose of the risk management system is to ensure the achievement of the company's goals regarding:
The specific risk management strategy is an integral part of the company’s general strategy, with the following fundamental objectives: meeting the SCR and MCR capital requirements and ensuring a high solvency ratio, achieving an optimum reinsurance programme and efficient management focused on profit and capitalization, all serving the single purpose of maintaining PAID S.A.’s financial stability so that all its financial obligations to the Client are fulfilled.
PAID S.A. annually creates a Risk plan which underlines objectives and measures for each significant risk, which is sent to the Board of Directors for debate and approval.
PAID’s risk strategy is based on the following principles:
The company’s main strategic goals are still related to the company’s 4 pillars of sustainable development, namely:
1. Governance: ensuring an operating framework fully consistent with legal requirements and the risk profile of the company;
2. Financial sustainability: reflected by the company's solvency ratio and the appropriate size of the structure and level of reinsurance protection;
3. Operational sustainability: reflected in the ability to handle a much higher volume of operations than the usual average at any time in case of major events or expanding the portfolio;
4. Development: increase of the penetration rate and implicitly growing the portfolio.
PAID S.A.’s activity is analyzed in terms of exposure to the following risks: underwriting risk, liquidity risk, credit risk, market risk, operational risk, reputational risk and strategic risk. Risks are handled both individually and cumulatively. PAID S.A. calculates the capital requirement using the standard formula. The results obtained give an overview of how risks are divided into various risk categories and establish capital and solvency requirements in accordance with Solvency II.
Based on the financial results in the past few years, PAID S.A. accumulated own funds since no significant events occurred. The events at the beginning of 2023 caused major reinsurance pricing rises and significantly higher damage costs, leading to a weaker technical result in 2023 and indicating a potential for increased reinsurance rates.
Risk analyses are carried out at company level following the requirements of risk
policies and procedures.
The quantitative assessment of the Solvency Capital Requirement is as follows:
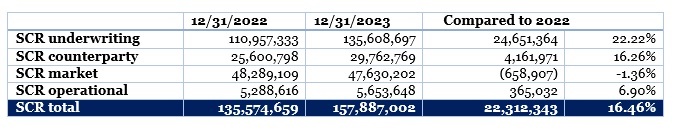
More details on the risk management system are available in the Solvency and Financial Condition Report (SFCR) Chapter B (subchapter B.3) și Chapter C.
F. Conclusions of the assessment of the risk management system efficiency